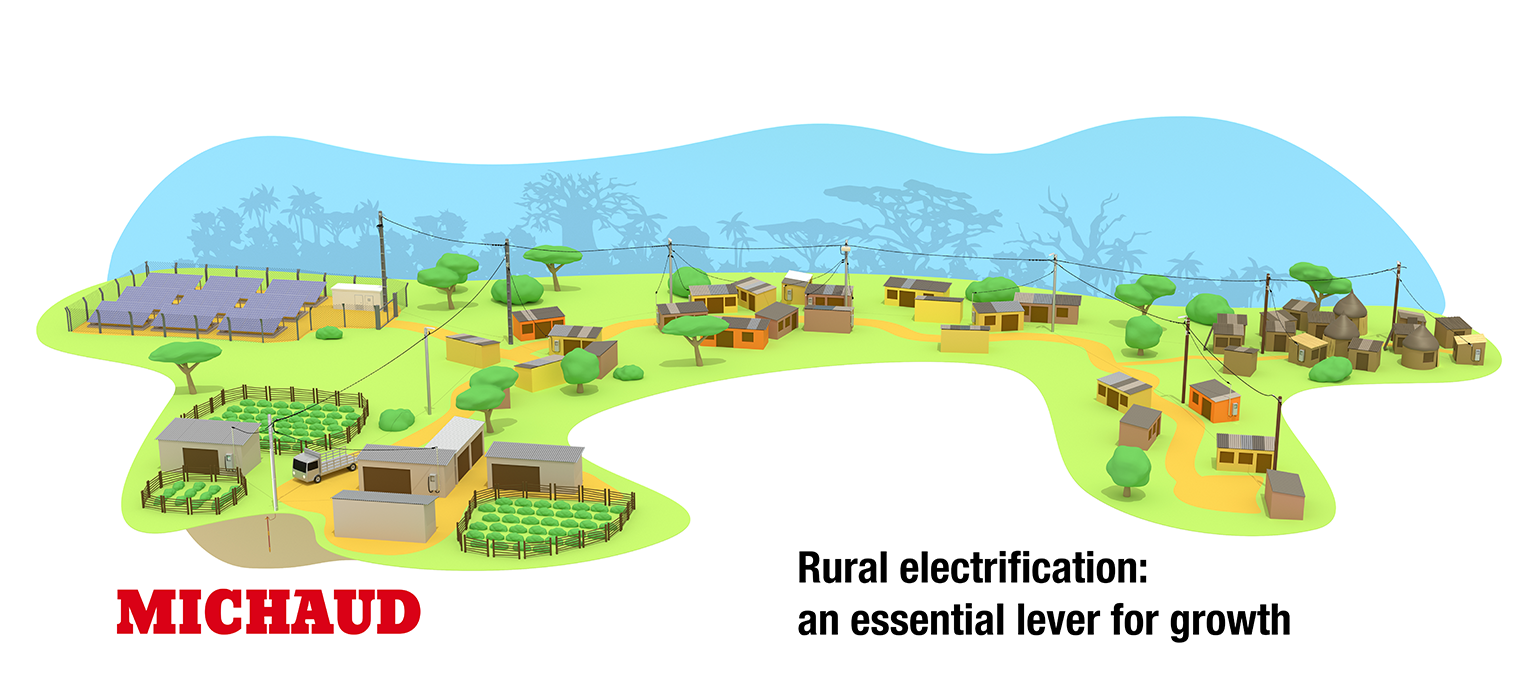
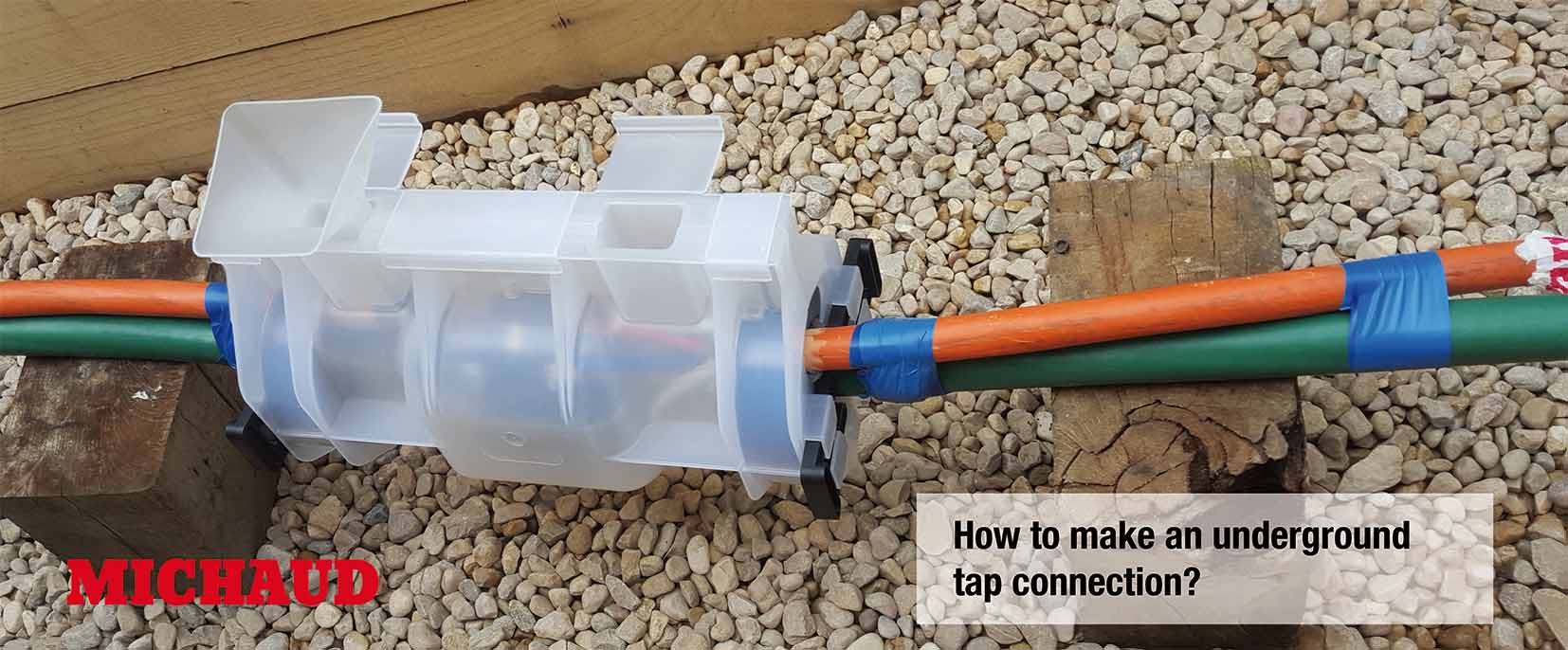
Rural electrification encompasses all the technical, economic and social actions required to bring electricity to rural areas, which are often remote or difficult to access. This process is crucial to improving the quality of life of local residents and stimulating the local economy. Rural electrification can be broken down into three main areas: extending the network, reinforcing existing infrastructures and concealing installations to preserve the aesthetics of the landscape.
Extending rural electrification: connecting isolated areas
Reinforcing existing electrical infrastructure is a fundamental element of rural electrification. This includes upgrading transformer stations, replacing obsolete cables with more efficient ones, and optimizing equipment to reduce energy losses. Reinforcing the network also paves the way for the integration of renewable energies such as solar and wind power, while ensuring a more stable and reliable power supply for rural areas.
Concealing installations: preserving the environment and aesthetics
Concealing electrical installations is an integral part of rural electrification projects. By burying power lines or camouflaging poles and transformers, this method reduces the visual impact of infrastructures and preserves the aesthetics of rural landscapes. In addition, undergrounding protects installations from the elements and reduces the risk of vandalism, while helping to protect natural and heritage areas. Although it involves additional costs, concealing installations improves safety and enhances residents’ quality of life.
The benefits of rural electrification: an economic, social and ecological impact
Economic impact
Electrification of rural areas plays a key role in sustainable development. In economic terms, access to electricity encourages the creation of local activities, the mechanization of agriculture and crafts, and makes rural areas more attractive. Rural electrification also encourages new populations and experts to settle in these regions.
Social impact
In social terms, rural electrification improves living conditions by providing reliable energy for homes, schools and medical facilities such as hospitals and clinics. It also reduces inequalities between urban and rural areas by providing better access to education, health and connectivity.
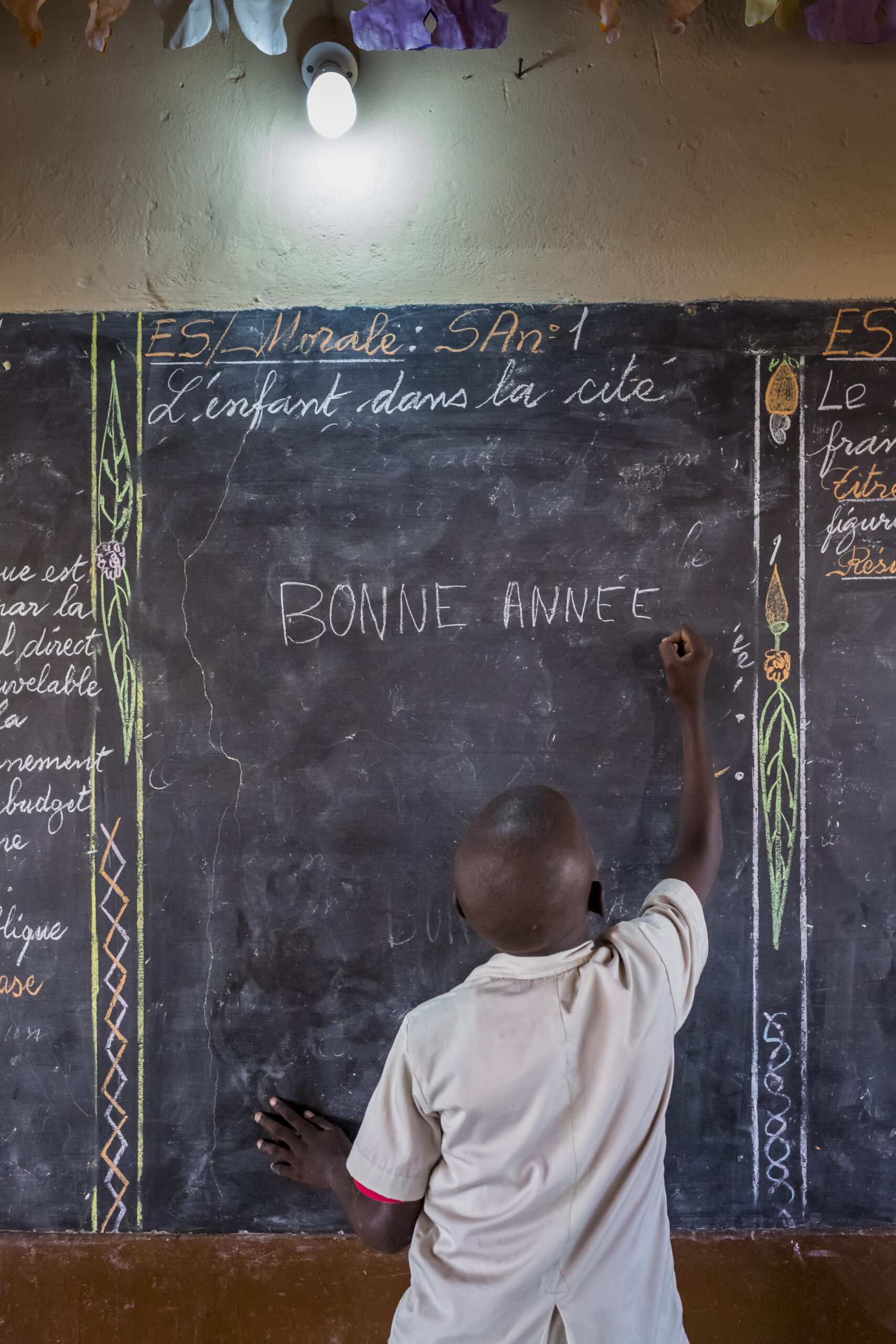
Ecological impact
From an ecological point of view, rural electrification reduces dependence on fossil fuels and greenhouse gas emissions. By integrating renewable energies into the grid, this approach supports a greener future for rural communities. Finally, initiatives such as burying power lines help preserve natural landscapes and heritage.
In conclusion, rural electrification is an essential lever for improving living conditions in isolated areas, while promoting sustainable development. By extending power grids, reinforcing existing infrastructures and integrating aesthetic solutions to preserve landscapes, this process makes it possible to meet the energy challenges of rural territories. What’s more, rural electrification plays a crucial role in social inclusion, economic growth and environmental preservation, offering rural populations opportunities equal to those in urban areas. By integrating renewable energies and modernizing infrastructures, rural electrification paves the way for a greener, more inclusive and more prosperous future for rural communities.